Disease characteristics
- It has a natural curve that removes some of the load from walking upright;
- Another part falls on the ribs and sternum, functioning as a physiological framework;
- This is the longest part of the spine (12 vertebrae), but the spinal canal is the narrowest;
- The thoracic vertebrae are smaller in size but have longer spinous processes;
- He is inactive.
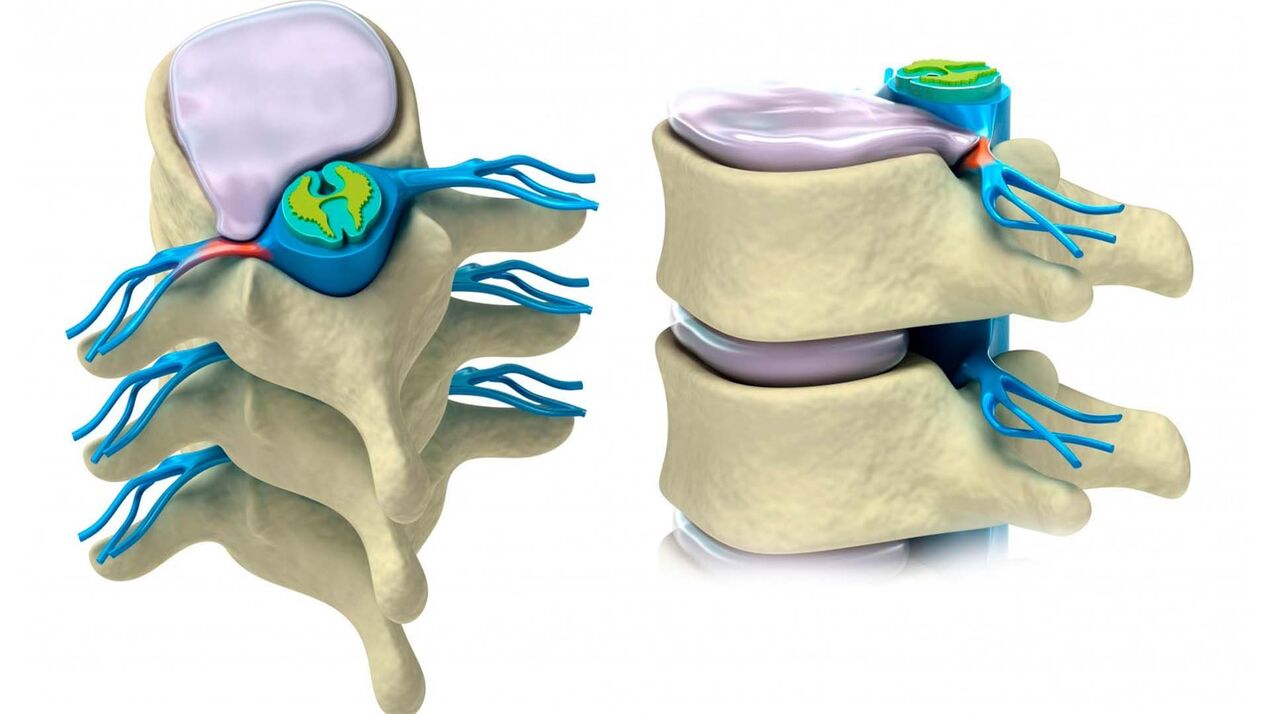
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
- pain. Nerve pain occurs in the upper back, between the shoulder blades, and around the intercostals. It gets worse when you cough, take deep breaths, and turn your body. Because there are many nerve fibers in the chest, chest pain (dorsago) can occur, much like a heart attack.
- Radiculitis. In addition to pain, there is also a loss of sensitivity. Usually the extremities, upper abdomen, and area below the collarbone become numb.
- feeling abnormal. There is a feeling of goosebumps all over the body.
- cardiac syndrome. Severe heart pain persists and does not go away even after taking medication.
- pulmonary syndrome. It manifests as suffocation and congestion in the lungs.
- abdominal syndrome. It is characterized by persistent pain in the digestive organs.
- muscle tension. It occurs reflexively in the upper back and chest.
In men, complications of the disease can affect potency.
Location of pain syndromes
- In thoracic osteochondrosis, symptoms of heart pain occur when the first to sixth thoracic nerves are affected. Women may have pain in their breasts.
- If thoracic nerves 6 to 9 are affected, stomach pain may occur. It feels the same as colitis and gastritis. There may be a sensation of a foreign body in the esophagus.
- In the small intestine, kidneys and genitals, if pathological processes affect the 11th and 12th intervertebral discs.
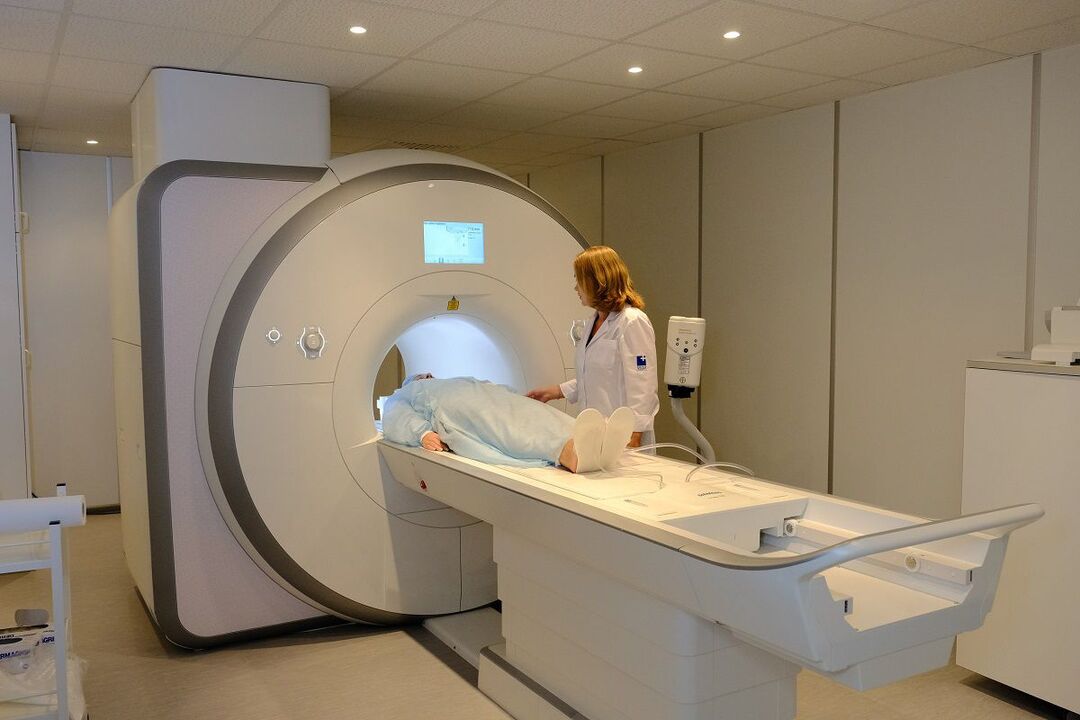
It is necessary for women to undergo radiography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, electrocardiography and mammography.
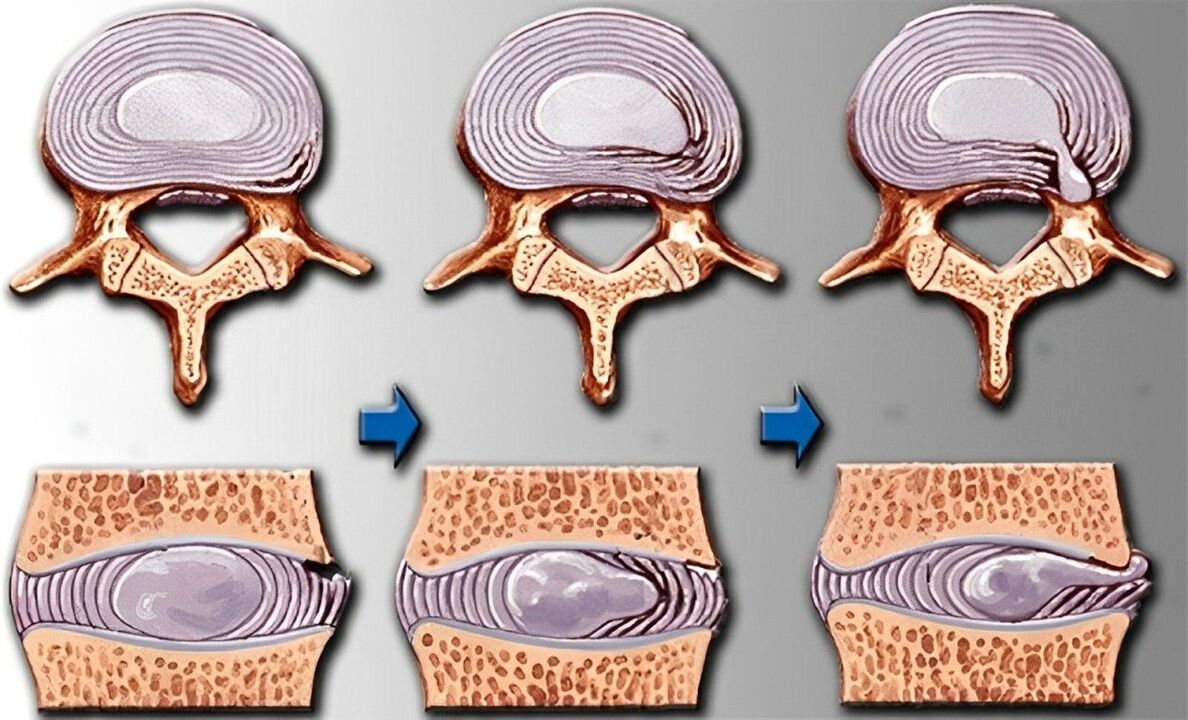
stage of disease
| stage | Variety | symptom |
| first | The disc becomes dehydrated, causing a loss of elasticity. Their height decreases, but their width increases—the discs gradually flatten. | The pain occurs directly over the damaged ring. It can be pulled or shot. |
| second | The annulus fibrosus begins to disintegrate. The nerve roots are compressed, causing pain. | Pain when moving. Discomfort occurs when you remain in one position for an extended period of time. |
| third | The annulus fibrosus ruptures, causing a herniated disc. Scoliosis or pathological kyphosis occurs. | Pain when moving. Discomfort occurs when you remain in one position for an extended period of time. |
| fourth | Friction occurs between the vertebrae, causing the intervertebral joints to shift. Inflammation of the tissue surrounding the vertebrae. Cartilage tissue is replaced by bone tissue, thereby reducing motor function. Fibrosis occurs. | Pain when moving. Discomfort occurs when you remain in one position for an extended period of time. |
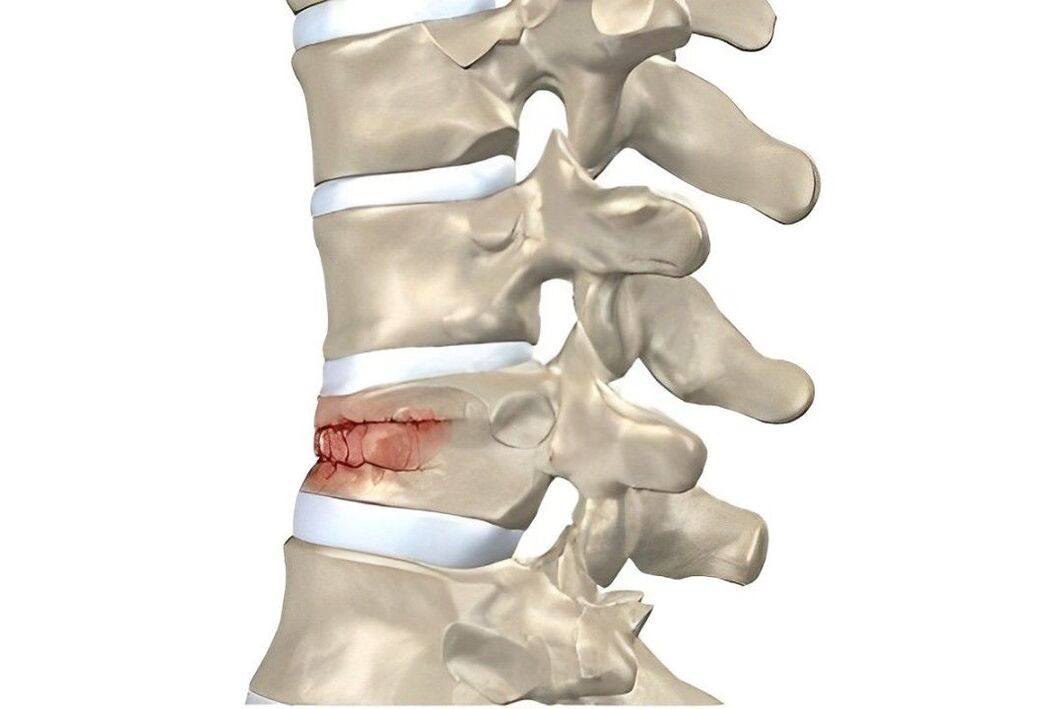
disease extent
| degree | changes and symptoms |
| first | Disc rupture caused by sudden movement or excessive force. Severe pain, similar to an electric current running down the spine. Muscle strain. |
| second | It is characterized by spinal instability. Pain when moving. protrude. |
| third | The pain becomes constant. Loss of feeling. Gait changes. Severe headache. Difficulty breathing. Tachycardia. |
| fourth | Spinal instability: The vertebrae slip and twist. Osteophytes grow, squeezing spinal nerves and putting pressure on the spinal cord. |
Thoracic osteochondrosis
Therefore, women need to undergo tests such as mammograms to confirm the diagnosis.
- Dorsago ("thoracic pain", "dagger pain") is a sudden, severe, severe pain in the chest (between the shoulder blades), most commonly after being in the same uncomfortable position for a long time. When you have chest and lower back pain, your muscles become tense and it becomes difficult to breathe. Back pain may worsen if you rotate your upper body.
- Chest pain is chronic mild pain in the breastbone. Chest pain can manifest not only as osteochondrosis, but also as diseases of the internal organs (lungs, heart, stomach) located in this area. The main difference in this type of pain in osteochondrosis is that the pain is superficial and segmental along the intercostal spaces. Chest pain caused by osteochondrosis can be worsened by movement and deep breathing and relieved by rest.
- Numbness and goosebumps in certain parts of the skin;
- Burning and itching sensation between shoulder blades;
- a cold feeling in the legs;
- Pain in the pharynx and esophagus;
- Stomach and intestinal dysfunction.
Treatment of female pathologies
What women with osteochondrosis feel like
- Pain in the heart area. In this case, the symptoms are more similar to heart disease, such as a heart attack or angina. The pain feels dull or aching and can last for months. However, vascular medications did not lead to improvement, and electrocardiogram results did not reveal any abnormalities.
- Breast discomfort. Most common in women, it is characterized by a constant feeling of pain. It is often confused with breast disease. In this case, a more detailed diagnosis is required.
- abdominal cramps and pain. It is characterized by typical symptoms of various pathological processes in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, which are often mistaken for gastritis, ulcers or cholecystitis. With the strengthening of body movements.
complications of disease
Osteochondrosis often affects multiple sectors gradually or simultaneously.
- cardiovascular system diseases;
- nutritional system;
- Digestion;
- respiratory system;
- faint;
- Dizziness;
- Panic and fear with rapid heartbeat and suffocation;
- chronic fatigue;
- Shingles.